Introduction
Jason Toews and Dustin Coupal noticed a need for a site to help people find the cheapest local gas prices and founded GasBuddy.com in June of 2000. At the time, Toews was working as a computer programmer and Coupal was an eye doctor. The partners nurtured the website over the course of the next decade, persuading drivers to log in and share gas prices – not an ideal situation, of course. Then, in 2009, the partners realized the potential of mobile apps. The company launched Android and iPhone apps later that year, which were instantly popular. Today, six million people have downloaded these apps.
Discover more
Conduct an online search for GasBuddy.com if you would like to explore this website.

Early on, these partners learned that financial institutions require properly prepared balance sheets to justify providing capital for growth, and that income statements are a mechanism for tracking performance over time. Although positive cash flow is one of the most important parts of their business, the partners have to ensure that all reports are prepared in a standardized manner.
Join the discussion
Participate in a discussion with your classmates.
Think of a local business or startup company you are familiar with. Identify three ways in which they can use accounting information.
Accounting fundamentals, principles, and practices
It’s not just small businesses that benefit from accounting. Large corporations also need accounting information for internal and external purposes. Let’s go back in time to the beginning of a company you may be familiar with: Nike.
The Nike athletic machine began as a tiny shop and a distributing outfit located in the trunk of a car in 1964. Phil Knight sold $8,000 worth of a shoe called the Onitsuka Tiger athletic shoe from Japan and placed an order for more. After achieving $1 million in sales and riding the wave of the success, Knight devised the Nike name and trademark “swoosh” symbol in 1971.

Onitsuka Tiger running shoe
By the late 1970s, Blue Ribbon Sports officially became Nike and went from $10 million to $270 million in sales. The 1980s and 1990s would yield greater and greater profits as Nike began to assume the appearance of athletic juggernaut, rather than the underdog of old. The magazine company, Ad Age, named Nike the 1996 Marketer of the Year. That same year Nike’s revenue was $6.74 billion. In 2021, its annual revenue was a staggering USD $44 billion.
Transferable skills
One of the skills we are practicing in this learning activity is Digital Literacy. We will be demonstrating a willingness and confidence to explore new or unfamiliar digital tools and emerging technologies.
Why is accounting important?
Definition
Accounting
Accounting is the process of identifying and recording a business’s economic events and transactions, and communicating them to a variety of interested users in report form.
Investors and stakeholders require these financial reports to be highly transparent, relevant, and dependable. If not, this can have catastrophic results for both the investors and the company. Poor accounting can cause a company to go out of business or fall into debt, owing money to banks and investors. In cases where laws are broken, senior managers may have to pay penalties or serve jail time.

So, you might be thinking that accounting is important only to those students who want to become accountants. What about learners who aren’t interested in this career path?
Understanding accounting essentials is crucial for everyone. By studying accounting, you will learn about the world of business, including different types of businesses and how they work.
You may plan to own your own business one day or invest in one (if you haven’t done so already). The way that you read, interpret, and analyze financial information will give you a valuable set of skills for making sound financial decisions.
By now, you may have realized that accounting knowledge is a powerful tool and a key ingredient for success, but how does knowledge give you power? What exactly does accounting focus on? In the next few topics, we will address these as well as other questions.
What makes accounting powerful?
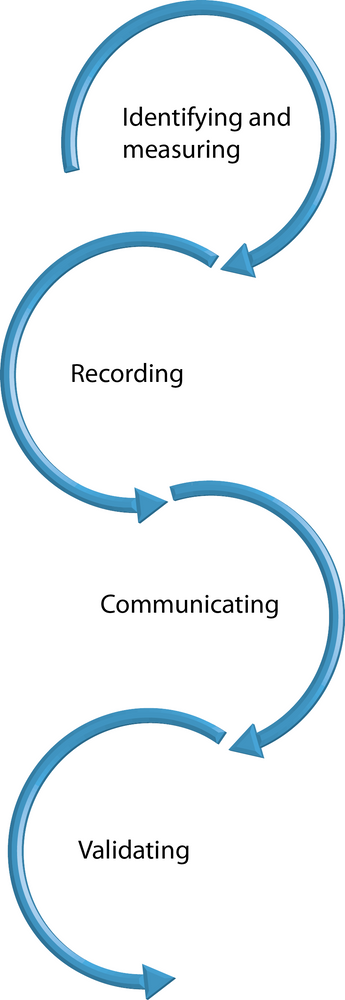
Accounting’s main objectives are identifying and measuring, recording, communicating, and validating. It involves collecting, recording, and reporting an organization’s financial situation to its various decision makers.
Accountants help people to make better financial decisions. They help them to assess prospects, products, and other opportunities. As well as reporting on a business’s performance, accountants also report on what the business owns and owes. Essentially, accounting is a tool that opens our eyes to endless possibilities.
The power of accounting: An example
TD Bank teams up with Starbucks to brew up an innovative customer experience
TD becomes the first major Canadian bank to invite a full-service retailer into a branch. Imagine the convenience of completing your daily banking and ordering your favourite beverage all under the same roof!


How do you think this partnership came about? Both parties used a powerful tool – accounting – to thoroughly analyze all of the information available in order to make their decision. Let’s face it: Both of these companies are well known, but they have different customer bases. Therefore, increasing customer exposure to both parties in this way will ensure positive results for both conglomerates involved.
What does accounting focus on?
Accounting affects all parts of our lives: mortgage applications, credit card applications, bank accounts, and car loans, to name a few. These examples, however, only involve the recordkeeping part of the accounting system. Bookkeeping/recordkeeping is the system used to record a company’s financial transactions. Accounting involves the recordkeeping process, but this is just one of its many applications.

Notebook
As a self-assessment exercise, respond to the following questions in your notebook. Use the suggested answers to check your understanding.
- Why is good accounting important? What problems can bad accounting cause?
Good accounting provides everyone involved in the business with accurate information about how the business is doing, where it is making money, where it is losing money, and how much it should pay in taxes. Bad accounting can have catastrophic effects for both investors and the company. It can cause a company to go out of business or fall into debt, owing money to banks and investors. In cases where laws are broken, senior managers may have to pay penalties or serve jail time.
- How can the study of accounting benefit you, even if you are not interested in an accounting career?
By studying accounting, you will learn how the world of business works. The way that you read, interpret, and analyze financial information will give you a valuable set of skills for making sound financial decisions as a business owner or investor.
Using accounting information
The two main groups/users of accounting information are internal and external users.
Internal users
Internal users use the information gathered to plan, organize, and operate their companies. Individuals such as managers of finance, production, and marketing, as well as human resources personnel, all use accounting to make crucial decisions.
In the daily running of an organization, internal users must answer similar questions. Press the following tabs to explore the kinds of questions they ask.
In order to answer these and many other questions, users require highly detailed and accurate information that is up to date. For example, they need to know information such as cash flow projections for the upcoming year, projected profits, and budgets.
Using accounting information
External users
These individuals are not involved in the daily running of the organization. Examples of external users are shareholders, lenders, directors, customers, suppliers, brokers, and the press. Each of the users mentioned has a special need for the information provided, depending on the decision they need to make.
In order to make certain decisions, specific key questions have to be answered:
Investors

Based on the company’s performance, will I get back what I have invested?
Creditors

Will the company be able to pay its debt?
Take a break!
Excellent work! You have just completed the section on the different types of accounting users. Now is a great time to take a break before you move on to the next section on accounting ethics, concepts and principles.
Understanding accounting ethics, concepts, and principles
Accounting ethics
Definition
Ethics
Ethics are moral principles that govern the way people behave. In business, ethics are generally accepted moral and professional principles used to differentiate right from wrong. Ethics are particularly important within the accounting profession, as well as in other professions dealing with finances. Lack of ethics in businesses has led to harm including economic, environmental, social and legal concequences.
Ethical practices build trust, which promotes loyalty and long-term relations between all parties involved. Good ethical practices enhance the organization’s reputation and success. This is why accounting principles are created, maintained, and followed.
A company’s financial information is communicated using various accounting reports, the most common being financial statements. Accountants prepare these statements using standardized guidelines, to make the information provided in them meaningful. Every profession creates its own standards based on ethics and norms, and accounting is no exception.
Accounting concepts
To use accounting information, we need to thoroughly understand the basic assumptions and principles of accounting in Canada, including the standards of the accounting profession.
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
The underlying ideas that make up acceptable accounting practices are called “Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).” These include broad principles and practices, as well as rules and procedures. GAAP are applied when the accounting information is recorded and reported. It is important to point out, however, that GAAP are not static; they change over time. For those fiscal years starting on or after January 1, 2011, Canada abandoned Canadian Generally Accepted Accounting Principles and adopted International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) as the preferred accounting standard. However, companies were allowed to adopt the U.S. GAAP, instead of IFRS. As a result, many small to medium-sized Canadian firms prepared reports using the U.S. GAAP after Canada had adopted IFRS. The companies that were more likely to choose IFRS were larger, or were in the startup stage, or had no (or few) U.S. operations. A third option, which is open only to not-for-profit organizations, is to follow the “not-for-profit (NFP) reporting standards.”
A little bit of history
In the past, these rules and guidelines were contained in the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAPs). GAAPs were applied consistently by all accountants for all businesses, making the accounting information meaningful and comparable by those who understand how accounting information is compiled. In Canada, the Canadian Institute of Chartered Accountants (CICA) published a handbook containing these principles. The CPA has replaced CICA and since then there have been many changes to the Canadian accounting industry.
In 2011, the Canadian GAAP was replaced by either the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) or the Accounting Standards for Private Enterprises (ASPE) set by the Canadian Accounting Standards Board (AcSB). IFRS are standards for businesses that are publicly traded on the stock exchange whereas the ASPE standards apply to businesses that do not have a public listing. (You will get an overview of different types of business ownership in this course). Professional accountants need to create financial statements that strictly follow these standards and as a result must have strong familiarity with them. Throughout this course, you will come across the standards “in action” as they apply to different accounting statements and functions.
Explore this!
Explore the following video to learn more about the differences between the U.S. GAAP and current accounting practices.
The term “generally accepted” means that the GAAP have authoritative support from both U.S. and Canadian banks, companies, and institutes. For example, the Chartered Professional Accountants (CPA) of Canada is responsible for developing accounting principles in Canada. (For more information on the CPA, do an Internet search using the terms “chartered professional accountants” and “CPA.”) CPA has primary responsibility for developing and issuing our GAAP. The Canada Business Corporations Act and the Ontario Securities Commission recognize these principles as the standards to follow for preparing and communicating financial information.
Accounting assumptions
Accounting assumptions are rule that ensure that the business operations of an organization are run efficiently and that the financial statements are consistent. Press the following tabs to learn more about key accounting assumptions.
Accounting principles
Accounting principles are rules and guidelines that a business must follow to when reporting financial data. Press the following tabs to learn more.
Notebook
As a self-assessment exercise, answer the following questions in your notebook. Use the suggested answers to check your understanding.
- What is the difference between external and internal users of accounting?
Internal users of accounting are those within a company, such as managers of finance, production, and marketing, as well as human resources personnel. External users include shareholders, potential investors, and creditors.
- How can the study of accounting benefit you, even if you are not interested in an accounting career?
Ethical practices build trust, which promotes loyalty and long-term relations between all parties involved. Good ethical practices enhance the organization’s reputation and its success. This is why accounting principles are created, maintained, and followed.
Conclusion
In this learning activity, you learned how businesspeople and companies use financial information to help them make investment decisions. You also learned about accounting ethics, concepts, and principles.
Portfolio
Thinking about the accounting standards and assumptions discussed in this learning activity, identify how the various transferrable skills will be utilized and developed. Try to place yourself in the role of an accountant or business owner when identifying which transferrable skills apply to each accounting standard.
Review the seven transferable skills in the following section to help inform your responses. Record a few points for each of the seven transferable skills as they relate to business and the accounting world.
Connecting to transferable skills
Recently, Ontario worked with other provinces in Canada to outline a set of competencies that are requirements to thrive. Ontario then developed its transferable skills framework as a set of skills for students to develop over time. These competencies are ones that are important to have in order to be successful in today’s world.
Read through the framework and the student look-fors (Opens in new window). Copy this document into your notes - you'll refer to it in each unit.
Note the indicators that you think you will develop in this course. At the end of the course you will revisit these skills to see which ones you actually developed and if your original predictions were correct.
As you continue through this unit and the rest of the course, keep your notebook updated and be mindful of opportunities to apply and develop transferable skills.
Take a break!
Excellent work! You have just completed this learning activity. Now is a great time to take a break before you move on to the next one.